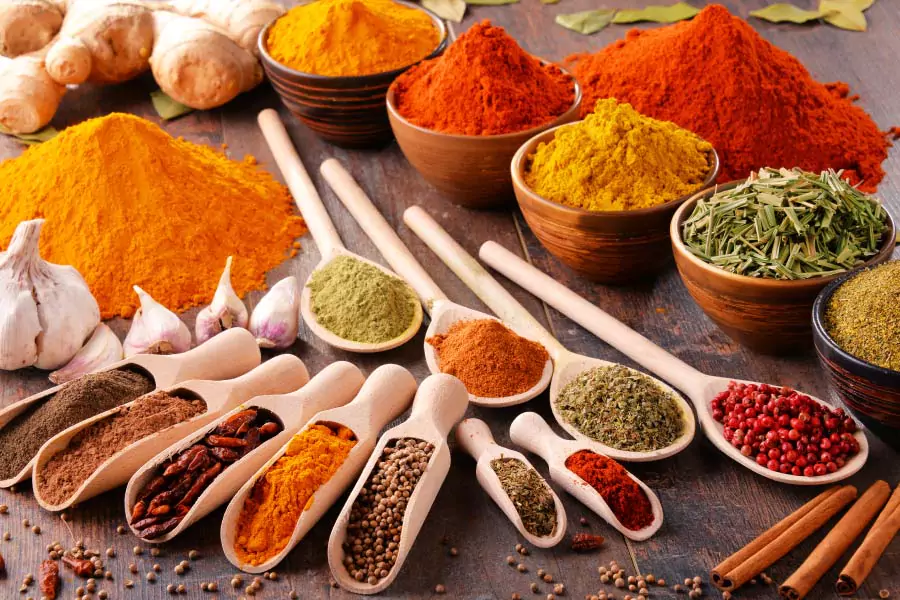
Phosphine
Phosphine is a toxic gas used for pest control by fumigation.
Cadir Lab has developed a method for the determination of phosphine residues on cereals using headspace coupled with gas chromatography, to comply with the legal limits even for products intended for children (10ug / kg).
Phosphine (also called phosphane, hydrogen phosphide, hydrogen phosphorus or phosphorus trihydride) is a highly toxic gas. It can kill easily even at relatively low concentrations.
Uses in the agri-food sector
Phosphine gas is mainly used for pest control by fumigation. On farms it is often used in the form of aluminum phosphide pellets, which produce phosphine in contact with atmospheric water. These pellets also contain other chemicals that develop ammonia helping to reduce the potential for self-ignition or explosion of the toxic gas. They also contain other agents, mainly mercaptans, which give the phosphine a characteristic garlic odor, revealing its presence in the atmosphere. Especially for cereals and dried food products, fumigation occurs by saturating the storage cells or transport tanks with the developed gas.
Rules for use in laboratories
The use of phosphine is subject to an authorization from the competent Police Headquarters and the laboratory technicians who carry out the analyzes must be in possession of special licenses for the use of technical gas.





